Что такое хедж фонд?
Содержание:
- The Immediate Aftermath
- HFR Custom Indices & Data
- Credentialing for Hedge Fund Managers
- What is a Hedge Fund Manager?
- Как устроены хедж-фонды и для чего они нужны
- Taxing Hedge Fund Profits
- Private Equity Funds
- Фонды в России
- What Is a Global Macro Hedge Fund?
- Where Does that Leave Us?
- Hedge Funds
- Why Go Public?
- Сущность
- История
- Examples of Publicly Traded Hedge Fund Companies
- What Is a Hedge Fund?
- Global Macro Hedge Fund Example
- Стратегии хедж-фондов
The Immediate Aftermath
During and just after the 2008 crisis, some hedge fund supporters also argued that these firms were not the only ones participating in subprime securities. Perhaps as a result of these positions, the 2008 House Committee hearing on Oversight and Government Reform did not blame hedge funds out and out for the crisis. However, as time went on, some analysts offered alternate explanations which did place hedge funds more squarely at the root of the crisis.
Regardless of the role that hedge funds may have played in generating the crisis, they were nonetheless impacted by it. Along with other areas of the financial world, hedge funds faced the potential for increased regulation and industry criticism in the wake of 2008. According to Value Walk, by the end of 2008, there were more than 5,100 active hedge funds around the world. Interestingly, the first few years after the 2008 crisis did not slow down the launching of new funds; an additional 5,900 funds were launched through the end of September of 2014.
HFR Custom Indices & Data
HFR is a global leader in the creation of custom & customizable performance benchmarks for leading financial institutions and institutional investors. Custom indices can be optimized and tailored to meet any specific client requirements and specifications, including exposures to strategies, sub-strategy composition, currency hedging (any underlying, frequency or timing), fund size, parameters for fund inclusion or any other variable which can serve as a critical basis of indexation for your clients. Let HFR tailor your benchmark exposure to suit your or your client’s specific needs.
Credentialing for Hedge Fund Managers
In addition to regulatory licenses, hedge fund managers will often benefit from professional designations and credentials that can build trust among investors that the portfolio manager is skilled and knowledgeable.
The Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation is regarded by most to be the key certification for investment professionals, especially in the areas of research and portfolio management. Because of the time, discipline, and dedication it takes to pass the exams and become a member, charterholders often stand out. Earning the designation becomes even more critical as the workforce becomes more competitive.
For funds that trade actively based on technical indicators or momentum strategies, a Chartered Market Technician (CMT) designation is appropriate. Among industry practitioners, the CMT designation is widely considered the gold standard in technical analysis globally.
In addition to professional designations, having a graduate degree such as a masters or Ph.D. in a related field like finance, economics, or statistics can greatly help one’s capacity as a hedge fund manager.
1:04
What is a Hedge Fund Manager?
A hedge fund manager is firm or an individual who manages, makes investment decisions, and oversees the operations of a hedge fund. Managing a hedge fund can be an attractive career option because of its potential to be extremely lucrative. To be successful, a hedge fund manager must consider how to have a competitive advantage, a clearly defined investment strategy, adequate capitalization, a marketing and sales plan, and a risk management strategy.
Key Takeaways
- A hedge fund manager is a financial company or individual that employs professional portfolio managers and analysts in order to establish hedge funds.
- Hedge fund managers typically earn above average compensation, often from a two-and-twenty fee structure from investors.
- Hedge fund managers typically specialize in a particular investment strategy that they then use as their fund portfolio’s mandate.
1:04
Как устроены хедж-фонды и для чего они нужны
Определение в Википедии гласит, что это «инвестиционный фонд, ориентированный на максимизацию доходности при заданном риске или минимизацию рисков при заданной доходности». Чтобы понять, как работает этот инструмент, копнем поглубже.
Классическим примером хедж-фонда является Quantum, возглавляемый Джорджем Соросом. Последний прославился тем, что заработал миллиардную прибыль на шорте британского фунта в 1992 году. Также он известен инвестированием в российскую экономику, где потери от кризиса 1998 составили сумму, сопоставимую с выигрышем на фунте. Чтобы лучше представить себе, что такое хедж-фонд, пересмотрите фильм «Игра на понижение» («The Big Short»), снятый по книге Майкла Льюиса.
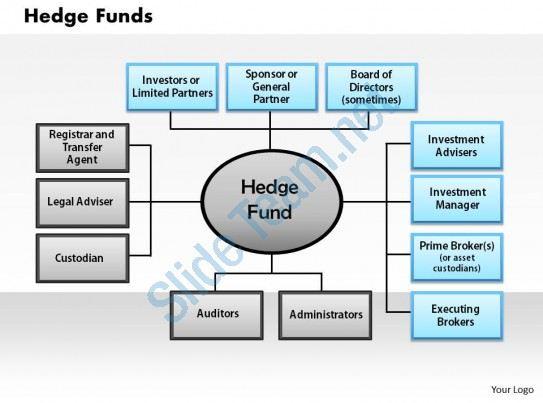
Главные элементы структуры хедж-фонда:
- Управляющий активами – УК, определяющая стратегию и операционное сопровождение;
- Кастодиант (обычно – банк-гарант по сделкам);
- Независимый аудитор – устанавливает стоимость активов и ведет бухгалтерию;
- Legal Adviser – обеспечивает юридическое сопровождение.
- Прайм-брокер (как правило, инвестиционный банк) – совершает сделки по поручению фонда, предоставляет в долг активы и ликвидность.
Одна из особенностей хедж-фондов – низкие регуляторные требования. Управляющие относительно свободны в выборе инструментов. Профессионалы, распоряжающиеся активами инвесторов, используют широкой пакет стратегий. Они включают кредитное плечо и сложные производные инструменты. Этим объясняется то, что доступ для непрофессиональных инвесторов (nonqualified investors) очень ограничен, а в большинстве случаев он полностью закрыт. Как правило, вкладчик не может вложить менее миллиона долларов (в Европе от $100 тыс.), а число участников не должно быть более 100.
Результатом хеджирования может явиться не только сдерживание рисков потерь, но и ограничение возможной прибыли. Ведь если вы угадали движение цены, то открытие сделки в противоположном направлении поставит стоп на этом верном курсе. Для чего же проводятся такие операции? Ответ очевиден: фонды имеют дело с деньгами клиентов и используют большое кредитное плечо. В этих условиях средства инвесторов нуждаются в страховке, а фонд получает свой профит в виде комиссии за управление.
Taxing Hedge Fund Profits
When a domestic U.S. hedge fund returns profits to its investors, the money is subject to capital gains tax. The short-term capital gains rate applies to profits on investments held for less than one year, and it is the same as the investor’s tax rate on ordinary income. For investments held for more than one year, the rate is not more than 15% for most taxpayers, but it can go as high as 20% in high tax brackets. This tax applies to both U.S. and foreign investors.
An offshore hedge fund is established outside of the United States, usually in a low-tax or tax-free country. It accepts investments from foreign investors and tax-exempt U.S. entities. These investors do not incur any U.S. tax liability on the distributed profits.
Private Equity Funds
Private equity funds more closely resemble venture capital firms in that they invest directly in companies, primarily by purchasing private companies, although they sometimes seek to acquire controlling interest in publicly traded companies through stock purchases. They frequently use leveraged buyouts to acquire financially distressed companies.
Unlike hedge funds focused on short-term profits, private equity funds are focused on the long-term potential of the portfolio of companies they hold an interest in or acquire.
Once they acquire or control interest in a company, private equity funds look to improve the company through management changes, streamlining operations, or expansion, with the eventual goal of selling the company for a profit, either privately or through an initial public offering in a stock market.
To achieve their aims, private equity funds usually have, in addition to the fund manager, a group of corporate experts who can be assigned to manage the acquired companies. The very nature of their investments requires their more long-term focus, looking for profits on investments to mature in a few years rather having the short-term quick profit focus of hedge funds.
Фонды в России
Ахиллесова пята российского рынка — его молодость. Существование инвестиционных фондов на законодательном уровне было закреплено в 2008 году «Положением об инвестиционных фондах». Хедж фонды России признаны отдельной категорией ПИФов.
Открыть хедж фонд в нашей стране проблематично из-за сложных правил регистрации — по данным сайта investfunds.ru официально зарегистрировано всего 24 организации.
Для российских структур характерны черты, присущие молодому, неразвитому рынку:
- повышенная степень закрытости крупных, известных игроков;
- высокая доля мошенников;
- отсутствие доверия к управляющим;
- ярко выраженный дефицит инвесторов.
- проблемы с покрытием операционных затрат и недостаточное финансирование в области исследований и анализа рынков;
- проблемы с квалифицированными кадрами, повышенный спрос на хороших трейдеров.
Среди российских организаций можно выделить следующие:
- УК: «Альфа Капитал». «Фонд частных инвестиций». Год основания: 2009. Носит закрытый характер. Позже под эгидой этой же УК был создан «Фонд корпоративных инвестиций».
- УК: «Europe Finance». Фонд «Dominum Russia Global». Год основания: 2009. «DRG» использует популярную западную стратегию управляемых фьючерсов.
- Основатель: ФК «Открытие». УК «Meriden IFM». Открытый стратегический фонд «Otkririe Hedge Fund». Зарегистрирован в 2007 году в Андорре. Ориентирован на работу с российскими активами на базе собственных мультистратегий.
- Определенный интерес также представляют организации, основанные ПАО «Сбербанк» и «ВТБ», а также: VR Global Offshore Fund, Diamond Age Atlas Fund, Copperstone Alpha Fund, Burnem Asset Management.
Помимо «чистых» хедж фондов в России можно выделить их ближайшие аналоги по своей экономической сущности: доверительные управляющие и общие фонды банковского управления (ОФБУ).
В роли УК ОФБУ выступает банк, лицензию выдает ЦБ РФ. Имущество ОФБУ полностью обособлено от имущества банка. Подобная организация деятельности дает ряд преимуществ:
- Возможность эффективного использования банковской инфраструктуры: депозитарий, банковский аудит и финансовый контроль, филиальная сеть. Это снижает комиссионные расходы инвестора.
- Хорошая надежность и прозрачность. Отдельный корреспондентский счет для вкладчиков в банке России и отдельный валютный счет в банке, указанном ЦБ РФ. В случае дефолта банка его вкладчики не претендуют на имущество фонда.
Процедура участия: инвестор вкладывает средства в обмен на сертификат долевого участия, не являющийся ценной бумагой, но дающий право на часть имущества. В отличие от ценных долевых бумаг (акций), сертификат не торгуется на рынке, но может быть завещан или просто переоформлен на третье лицо (на основании заявления в банк).
Требования к банку:
- срок «жизни» — не менее 1 года;
- величина капитала — от 100 млн руб.;
- рейтинг состояния — «финансово стабильный»;
- в бумаги одного эмитента может быть инвестировано не более 15% портфеля (кроме государственных бумаг).
What Is a Global Macro Hedge Fund?
Global macro hedge funds are actively managed funds that attempt to profit from broad market swings caused by political or economic events. Global macro hedge funds are market bets around economic events. Investors use financial instruments to create short or long positions based on the outcomes they predict as a result of their research. A market bet on an event can cover a wide variety of assets and instruments including options, futures, currencies, index funds, bonds, and commodities. The goal is to find the right mix of assets to maximize returns if the predicted outcome occurs.
Key Takeaways
- Global macro hedge funds make investment choices based on the broad economic and political outlook for various countries.
- Holdings might be long or short positions in different equity, fixed income, currency, commodity, or futures markets.
- The holdings in the funds are often positioned around a specific result of international economic or political issues, but the holdings can also be set up so the fund profits from general market volatility.
- Global macro strategies are either related to currency, interest rates, or stock or equity indexes.
- Global macro hedge funds include the discretionary, commodity trading advisor, and systemic categories.
Where Does that Leave Us?
For some analysts, this represents either hope for the continued survival of the hedge fund as a financial institution, or even a sign that hedge funds are making a comeback (the best-ever first-month performance for a hedge fund was Michael Gelband’s ExodusPoint Capital Management, launched in June of 2018). Regardless, as investors have grown increasingly interested in low-cost, often more stable types of investment—exchange-traded funds, index funds, and the like—hedge funds have lost some of the position of prominence that they enjoyed prior to 2008, perhaps never to get it back.
Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are alternative investments that use pooled funds and employ a variety of strategies to earn returns for their investors. The aim of a hedge fund is to provide the highest investment returns possible as quickly as possible. To achieve this goal, hedge fund investments are primarily in highly liquid assets, enabling the fund to take profits quickly on one investment and then shift funds into another investment that is more immediately promising. Hedge funds tend to use leverage, or borrowed money, to increase their returns. But such strategies are risky—highly leveraged firms were hit hard during the 2008 financial crisis.
Hedge funds invest in virtually anything and everything—individual stocks (including short selling and options), bonds, commodity futures, currencies, arbitrage, derivatives—whatever the fund manager sees as offering high potential returns in a short period of time. The focus of hedge funds is on maximum short-term profits.
Hedge funds are rarely accessible to the majority of investors; instead, hedge funds are geared toward accredited investors, as they need less SEC regulation than other funds. An accredited investor is a person or a business entity who is allowed to deal in securities that may not be registered with financial authorities. Hedge funds are also notoriously less regulated than mutual funds and other investment vehicles.
In terms of costs, hedge funds are pricier to invest in than mutual funds or other investment vehicles. Instead of charging an expense ratio only, hedge funds charge both an expense ratio and a performance fee.
Why Go Public?
Going public is an interesting move for a hedge fund since many attract investors, in part, by touting the lack of disclosures, reports and public information. While going public subjects the fund to a greater degree of scrutiny, the portfolios themselves would still be shielded from the investing community – only actual performance and aggregate values need to be disclosed in the annual reports.
A fund that elects to go public can be traded like any other listed security, allowing the investing community to gain exposure to the profits and losses of an otherwise unattainable portfolio. Hedge fund initial public offerings (IPOs) are rare because many hedge funds are simply too volatile to achieve high valuations. This volatility also extends to those who purchase a publicly traded hedge fund security. Additionally, hedge fund managers are not concerned with generating shareholder value through stock appreciation the way a growing company might. Hedge fund managers tend to be focused on one thing: cash returns on their investments.
Сущность
Хедж фонд — что это такое простыми словами? Частный инвестиционный фонд, который:
- Управляется профессионалами в интересах инвесторов.
- Действует по агрессивной стратегии инвестирования.
- Не ограничен в выборе способов вложения средств, активно использует производные хеджирующие инструменты (деривативы) и их сочетания.
- Цель: ориентируется на минимизацию риска при жестко заданном инвесторами уровне доходности или максимизацию прибыли при заданном уровне риска.
Ключевые принципы:
- Принцип защиты интересов инвесторов.
- Принцип долевого участия или доверительного управления. Последнее значит, что, вкладываясь в хедж фонд, вы передаете свои деньги профессиональным управляющим и становитесь бенефициаром (выгодоприобретателем).
- Принцип свободного и неограниченного управления. Основан на минимальном государственном нормативном регулировании и контроле. Так, в США в работу организации не вмешивается даже Комиссия по ценным бумагам и биржам. С одной стороны, принцип гарантирует максимальную степень свободы. А с другой — вкладчик должен уметь самостоятельно защитить свои интересы (например, в случае махинаций трейдера).
Как следствие, хедж фонд отличается следующими особенностями:
- большая гибкость и возможность следовать любой стратегии инвестирования, в том числе агрессивной;
- большой выбор потенциально выгодных инвестиционных активов с ограниченной для прочих инвесторов доступностью: бумаги иностранных эмитентов, драгоценные металлы, биржевые деривативы (фьючерсы, опционы);
- неограниченный размер кредитного плеча;
- возможность применения самых современных финансовых технологий (fintech, blockchain);
- ограниченное право участия и жесткие требования к вкладчикам — фонды предназначены только для профессиональных инвесторов.
Квалифицированный индивидуальный инвестор в России должен отвечать одному из следующих требований:
- владеет денежными средствами, их эквивалентами, ценными бумагами и деривативами на сумму от 6 млн руб.;
- имеет трехлетний опыт работы в организации, совершавшей сделки на рынке ценных бумаг;
- за последний год провел сделок на 6 млн руб., ежеквартально совершая не менее 10 сделок;
- имеет высшее образование в области деятельности на рынке ценных бумаг.
Чтобы окончательно определиться со спецификой хедж фондов, рассмотрим их отличия от классических ПИФов.
|
Критерий |
Хедж фонд |
ПИФ |
|---|---|---|
|
Контроль государства |
Жесткие правила учреждения. Деятельность регулируется слабо |
Жесткий контроль и регулирование деятельности |
|
Порог входа |
От 100 тыс. долл. |
От 1 тыс. руб. |
|
Требования к инвестору |
Квалифицированный/Аккредитованный |
Любой |
|
Инвестиционные активы |
Любые ценные бумаги Имущественные активы Драгоценные камни и металлы Валюта Деривативы: форварды, фьючерсы, опционы |
Ценные бумаги, торгующиеся на национальном рынке Имущественные активы |
|
Стратегии инвестирования |
Длинные и короткие позиции |
Длинные позиции |
|
Вознаграждение фонда / затраты инвестора |
Комиссии от стоимости пая (1–2%) плюс процент от прибыли (20–25%) |
Процент от стоимости пая (2–5%) |
|
Способ выхода |
Паи не торгуются на рынке и могут быть переоформлены на третье лицо только с уведомлением УК (как правило, внутри фонда). |
Паи обращаются на вторичном рынке. |
История
Первый хедж-фонд был создан Альфредом Уинслоу Джонсом в 1949 году. А. У. Джонс был социологом, среди прочего, писал статьи для американских журналов. Идея заработать с помощью инвестиций пришла к нему во время работы над статьей для Fortune о технических подходах к рынку. Целью созданного в 1949 году фонда A. W. Jones & Со было инвестировать деньги (свои и друзей) не ради собственно обогащения, а чтобы получить средства на жизнь и возможность заниматься любимым делом. Сам Джонс занимался социальными проблемами, в частности, проблемами бедности. Его инвестиционная стратегия заключалась в том, что он покупал акции, цена на которые могла вырасти, одновременно открывая шорты на акции компании, цены на которые, по его мнению, должны были упасть. Это позволяло снизить риск. Кроме того, он нашел способ отслеживания акций с высокой вероятностью роста.
Стратегия оказалась выигрышной, с 1960 по 1965 год она составила 325 %, что на 100 % больше, чем у самых доходных паевых фондов. За десять лет стоимость инвестиций Джонса выросла на 670 %. Его ставка составляла 20 % от прибыли.
Успешная стратегия получила распространение, в 1968 году в США было уже 140 инвестиционных партнерств, которые Комиссия по ценным бумагам и биржам США отнесла к хедж-фондам.
Наибольшее развитие хедж-фонды получили со второй половины 80-х годов прошлого века. Тогда среди инвестиционных институтов выделился новый тип фондов, занимавшихся прогнозированием экономических и политических событий и, исходя из этого, формировавших свой инвестиционный портфель.
Наиболее популярным местом расположения фондов является Лондон, на который приходится 31 % этого рынка, затем следуют США с 27 %.
Examples of Publicly Traded Hedge Fund Companies
BlackRock (NYSE: BLK) is one of the biggest and respected investment management companies. Based in New York City, BlackRock invests all over the world across all kinds of asset classes and serves private clients from pension funds to corporations and sovereign wealth funds. In addition to managing several traditional mutual funds and ETFs, the company also runs alternative asset portfolios and investments. BlackRock currently has almost $7 trillion in assets under management (AUM) with a market capitalization of $89.85 billion.
BlackStone Group (NYSE: BX) (unrelated to BlackRock) is another investment management firm that includes is sizeable alternative investments group, with $571 billion in AUM, and caters mainly to high net-worth clients. Invesco (NYSE: IVZ) is similarly situated, with $1.14 trillion in AUM with roughly 15% of that dedicated to alternative investments.
Some investment firms are organized more like traditional hedge funds, but still offer shares to the public. Some of these include:
- Och-Ziff Management (NYSE: OZM)
- Oak Tree Capital Group (NYSE: OAK)
- KKR & Co. (NYSE: KKR)
- Apollo Global Management (NYSE: APO)
(For related reading, see «Hedge Fund Risks and Performance.»)
What Is a Hedge Fund?
Hedge funds are alternative investments using pooled funds that employ different strategies to earn active return, or alpha, for their investors. Hedge funds may be aggressively managed or make use of derivatives and leverage in both domestic and international markets with the goal of generating high returns (either in an absolute sense or over a specified market benchmark). It is important to note that hedge funds are generally only accessible to accredited investors as they require less SEC regulations than other funds. One aspect that has set the hedge fund industry apart is the fact that hedge funds face less regulation than mutual funds and other investment vehicles.
1:51
Global Macro Hedge Fund Example
Examples of global hedge fund activity were evident before the Brexit vote in 2016 when the United Kingdom voted to exit the European Union (EU). Global macro hedge funds that felt confident that Britain would vote to leave the EU took long positions in safe assets, such as gold, and chose short positions against European stocks and the British pound. Global macro hedge funds that were uncertain about the outcome took long positions in safe havens and other instruments that payout during market volatility. Some undoubtedly guessed wrong and took losses on the long position in European stock indexes as the British pound and other assets dipped immediately after the results were known.
Because the funds are typically actively-managed, they tend to require a bigger initial investment and bigger lifetime fees than passively-managed funds.
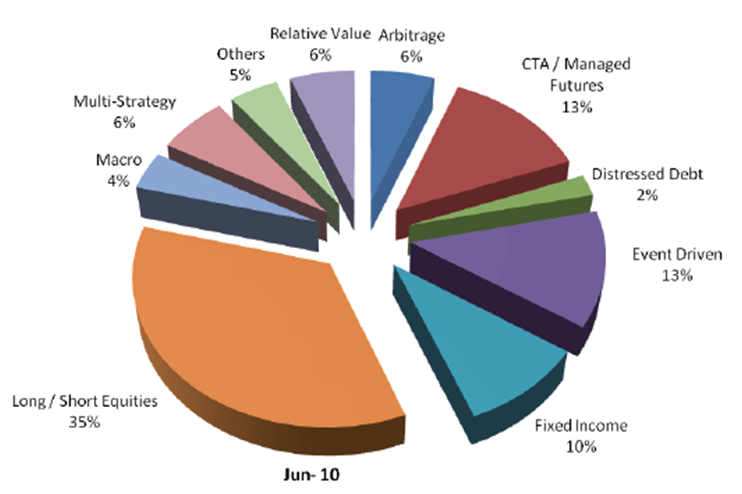
Стратегии хедж-фондов
Хедж-фонды применяют большое число стратегий для управления капиталом, однако преобладающей является ″Equity long-short″. Идея состоит в том, чтобы купить одни акции и, заняв короткую позицию, продать другие
Неважно, будет ли рынок расти или падать — важно, чтобы купленные акции росли быстрее или падали медленнее, чем проданные

Также довольно популярна Event-driven strategy, состоящая в спекуляциях на событиях, связанных с активностью компаний — например, слияние и поглощение, выделение дочерних компаний, реструктуризация и пр. Еще можно назвать Fixed income arbitrage strategy — это стратегия, при которой хедж-фонд зарабатывает на ценовых аномалиях, возникающих на рынке ценных бумаг с фиксированной доходностью, что можно рассматривать и как арбитраж. Наконец, популярна торговля фьючерсами и опционами, макроинвестирование с анализом глобальных макроэкономических процессов. Примерный баланс всего спектра стратегий можно увидеть ниже: